How to make the most of content groupings in Google Analytics
By Intern |1 Mar 2015
Content grouping is a great feature of Google Analytics (GA) that’s been around for a while now. It allows you to group content into a logical structure so you can analyse your website’s pages (or app) as part of your content marketing activity, without having to create advanced segments.
Once you set up Content Groupings you will be able to analyse and compare different types of content on your site, giving you aggregated data for content in each group. This feature is particularly useful if your website’s URLs do not follow a logical folder structure, thereby rendering the content drilldown reports useless.
Creating Content Groupings
GA does not automatically create a Content Grouping – there is no default setting unlike Custom Channel Groupings, meaning you have to set them up yourself.
Back in March 2014, when Content Groupings was a fairly new feature in GA, I posted a blog post ‘Content Grouping in Google Analytics – what you need to know’ . The blog post explained what you need to know about Content Groupings and includes a step-by-step video on how to set them up.
Summary of Content Groupings in GA:
- A grouping is a collection of groups
- A group is a collection of content
- You can create up to five content groupings in GA and switch between them in the reports
- Within each grouping you can have multiple content groups
- Content Groupings can be set up in three ways:
1. Group by GA tracking code – Extra code is added to the Google Analytics Tracking Code (GATC)
2. Group by extraction using regex – Use regex capture group to extract content by URL, page title, or content description value
3. Group using rule definitions – Define which pages belong to a group using defined rules
- While it’s possible to use all three methods for creating groups, you must remember that grouping logic is applied sequentially. This means, the tracking code method will be applied first, followed by the extraction method, and then finally the rules method will be applied
- Content Groupings are available in the All Pages and Landing Pages content reports as a primary dimension
- Content Groupings can also be used as a dimension in custom reports
- Content Groupings are not applied to historical data
- Content that is not included in a group will appear as (not set)
Top tip
Content Grouping rules are applied sequentially, so you should put specific grouping rules ahead of more generic rules to ensure content is correctly grouped. Arranging your rules in different orders will give you different results – be sure to plan and test your groupings
Top tip
If your CMS creates dynamic URLs, or the URLs you are trying to group do not have a common pattern, you will need to assign content groupings via the tracking code
Best practice for content grouping in GA
- Fresh Egg recommends that you test your content groupings in a test view before applying them to your reporting view
- Fresh Egg recommends that you add an annotation to GA once you apply the content grouping to the reporting view
- If you have previously used filters to simulate content grouping, Fresh Egg recommends using the content grouping feature in a new view that does NOT have the old filters applied
Which content should you group together?
This really depends on the kind of website that you have. There are two main choices; you can group content by page type or based on the page’s content.
By creating Content Groupings you will be able to analyse how different categories of products or areas of your site work together. To make the most of Content Groupings you need to group data that will be of most use to you when reporting on your KPIs – these should relate to your measurement plan. If you don’t have a measurement plan, get in touch with Fresh Egg to help you create one.
Here are some options for grouping your content:
- Navigation: If you have a good navigation structure with clean URLs, you could set up content groupings to reflect your top-level navigation
- Product Categories: If you have an ecommerce site, you may wish to group your content into product categories e.g. Women’s, Men’s, Home etc.
- Content Type: If you havea publishing site, you could group content based on category or subject type (e.g. news, weather, blog etc.)
- Customer Journey: If you have an ecommerce site, you may wish to group content to reflect the customer journey in order to understand the level of engagement at each of the key steps to purchase. To try to replicate this you could group your catalogue or list pages, product details pages and checkout pages etc.
- Audience Types: Is your content geared towards different audience types e.g. B2B vs B2C, Wholesalers vs Consumers? If so, this may be a beneficial way to group your content
- Error Pages: This group can contain all types of errors from login to 404 or incorrect data entry on a form
- Page Types: Grouping pages by page type or template enables you to review their performance more accurately. Fresh Egg uses page grouping for this purpose during conversion optimisation work, as it quickly identifies page types with a high level of ‘leakage’ – potential customers dropping out of the conversion journey. Typical page types in this group would be product pages, category pages, product listings, blog pages, checkout pages etc.
Top tip
Content Groupings are only available after you set them up, they cannot be applied retrospectively.
Top tip
Content Groupings cannot be deleted. You can switch them on and off but you can edit them – if you choose to edit them Fresh Egg recommends you annotate GA to reflect the changes you have made. If you do NOT annotate GA there will be no other record of the change.
Google Tag Manager and Content Groupings
If you have a Google Tag Manager (GTM) implementation of GA, you’ll be pleased to know that Content Grouping via the tracking code method can now be implemented through GTM. This was not available when I wrote my previous blog post, but is now.
How to set up Content Groupings in Google Tag Manager
Firstly, you will need to create the Content Grouping in the GA Admin section and select Content Grouping:
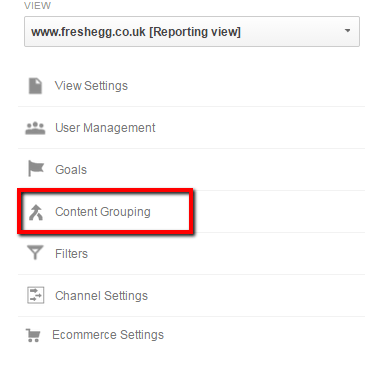
Then you need to select +New Content Grouping, give your new content grouping a suitable name and then select +Enable Tracking Code (this is required for the GTM set up):
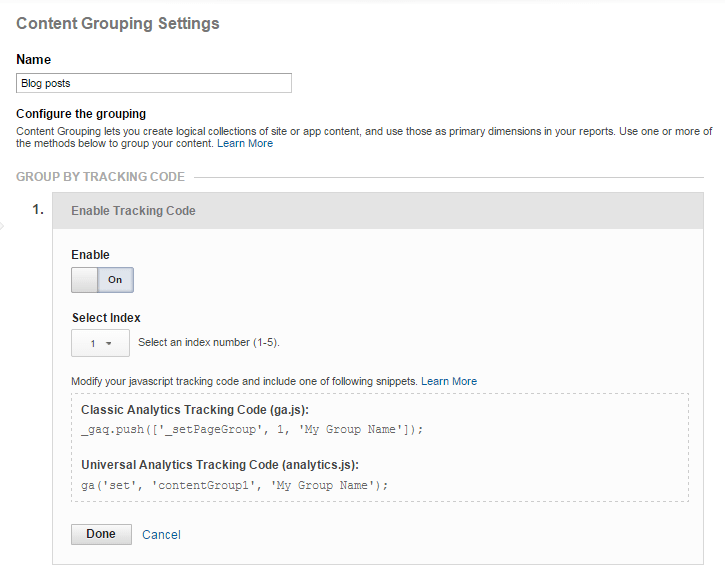
You will also need to select the index number (1-5, as you can create a maximum of five Content Groupings in GA). When you are ready click ‘Done’.
Top tip
Make a note of the index number as you will need this for GTM.
Modify your GTM tags
To add the code for Content Groupings via GTM, you’ll need to add the index and group name to a Page View tag in GTM. We’ve chosen to use the new interface to showcase this functionality.
You will need to use the URL structure of your pages to fire a separate Page View for those sections.
In this example we have created a Grouping called blog posts and want to group our blog posts by service (e.g. Analytics, CRO, Social etc.).
Create a trigger to match analytics blog posts
The trigger will be setup to match pages containing the ‘analytics-and-conversions’ category in the URL structure:
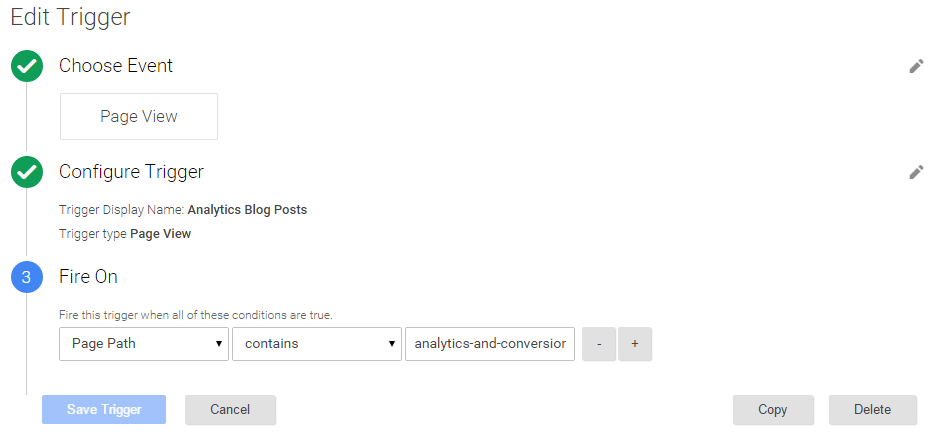
In the example above we have:
- Used a trigger type of ‘Page View’
- Given our trigger a useful name, “Analytics Blog Posts”
- Used the built-in variable ‘Page Path’ to check whether it contains ‘analytics-and-conversion’
Top tip
You can use the pages report in GA to test your trigger as a filter, to ensure it includes all the relevant pages.
Create a new Universal Analytics Page View tag
This will fire Page Views only for the specified content group.
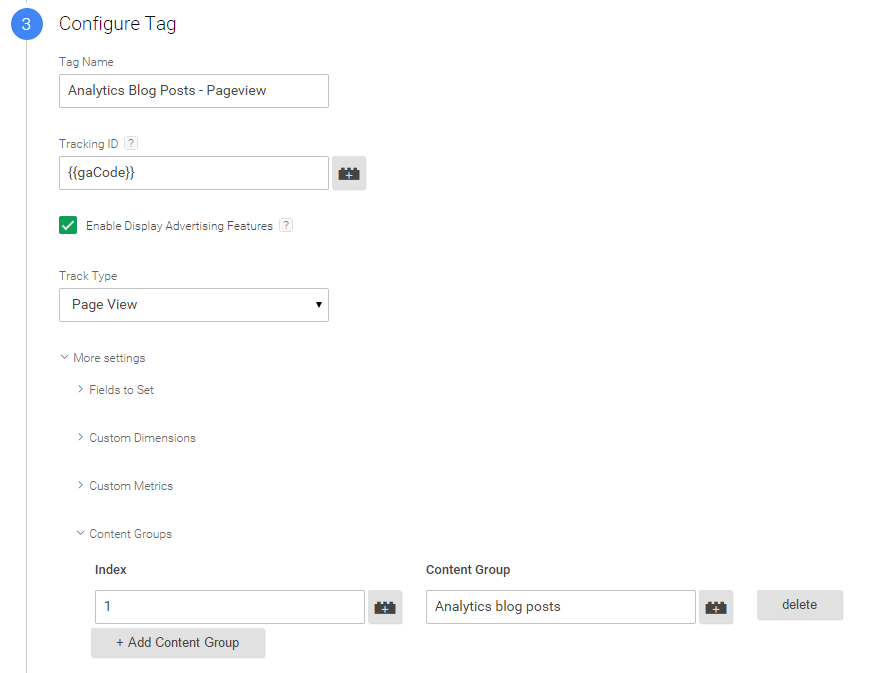
In the example above we have:
- Given our tag a clear and functional name “Analytics Blog Posts – Pageview”
- In More settings -> Content Groups we have added the index number and the value of this content group
- Selected the trigger we set up earlier, “Analytics Blog Posts” to fire this Page View only on this content group
Exclude analytics blog posts in standard Page View tag
We’ve set up a separate Page View tag for this group of pages, we need to ensure these are excluded in our main Page View tag or we would fire double Page Views.
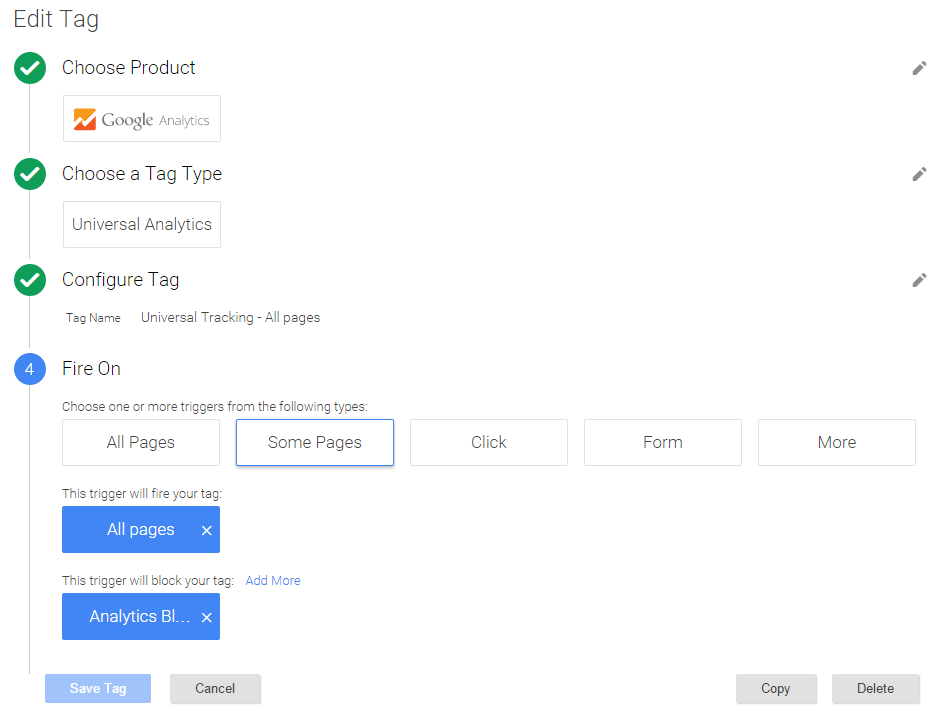
In the example above we have:
- In the “Fire On” section we’ve clicked ‘Create Exceptions’ and selected our “Analytics Blog Posts” as a blocker for this tag
- Blocking triggers will always take precedence over firing triggers
Top tip
Fresh Egg recommends that you test your setup and use the Preview and Debug mode in GTM to verify any changes.
Content Groupings and custom reports
One of the great advantages of using content groupings is that they are available in custom reports and dashboards too, giving them even greater flexibility.
Below I have set up a custom report to show page metrics for the navigation content grouping:
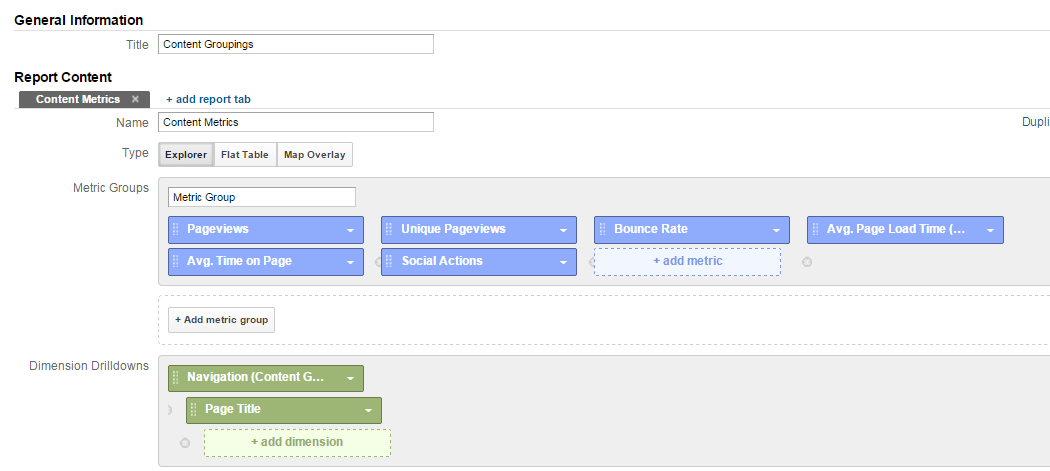
When you look at the report you will see something like this:
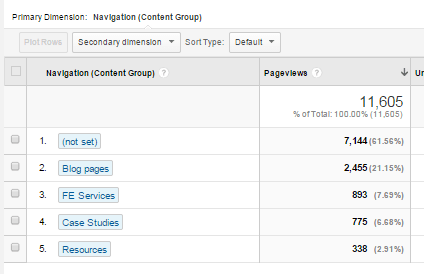
You can then create a new tab for each of your Content Groupings.
Top tip
Content Grouping dimensions are hit-level dimensions, so can only be used with hit-level metrics such as Page View, time on page etc. You can’t use them with session-level metrics, such as conversion rate or revenue per visit.
Do you trust your Google Analytics data? Can you get all the information from GA that you need to make important decisions about advertising, conversion optimisation and content creation?
Get in touch to talk to us about the challenges you face and how we can help you to get the most out of Google Analytics.